River bridges are essential infrastructures that have significant social and economic impacts. Because of the severe consequences of bridge failure, a particular care should be paid when designing such complex structures. Likewise, considering the large number of aging, existing river bridges and the increasing challenges posed by climate change and anthropization of catchments, it has become more and more important to define/clearly assess new strategies/criteria to reduce their vulnerability. In this frame, it is worth remarking that, because of the relevant importance of the mentioned structures, many studies, manuals and technical reports have been conducted/presented during the past years. However, despite the relevant efforts put by the international scientific community, most of the available literature on the topic clearly evidences that significant uncertainties still affect the design of such crucial infrastructures. As an example, it is well known that scour processes occurring in correspondence with bridge piers represent one of the primary causes of bridge failure. A recent study has evidenced that 52% of bridge failures are still caused by hydraulic-related issues, and most of them are due to excessive, localized erosion. This already critical condition is further exacerbated by new challenges connected to the increase of frequency of extreme precipitation and flood events, for which we are still in need for reliable predicting tools.
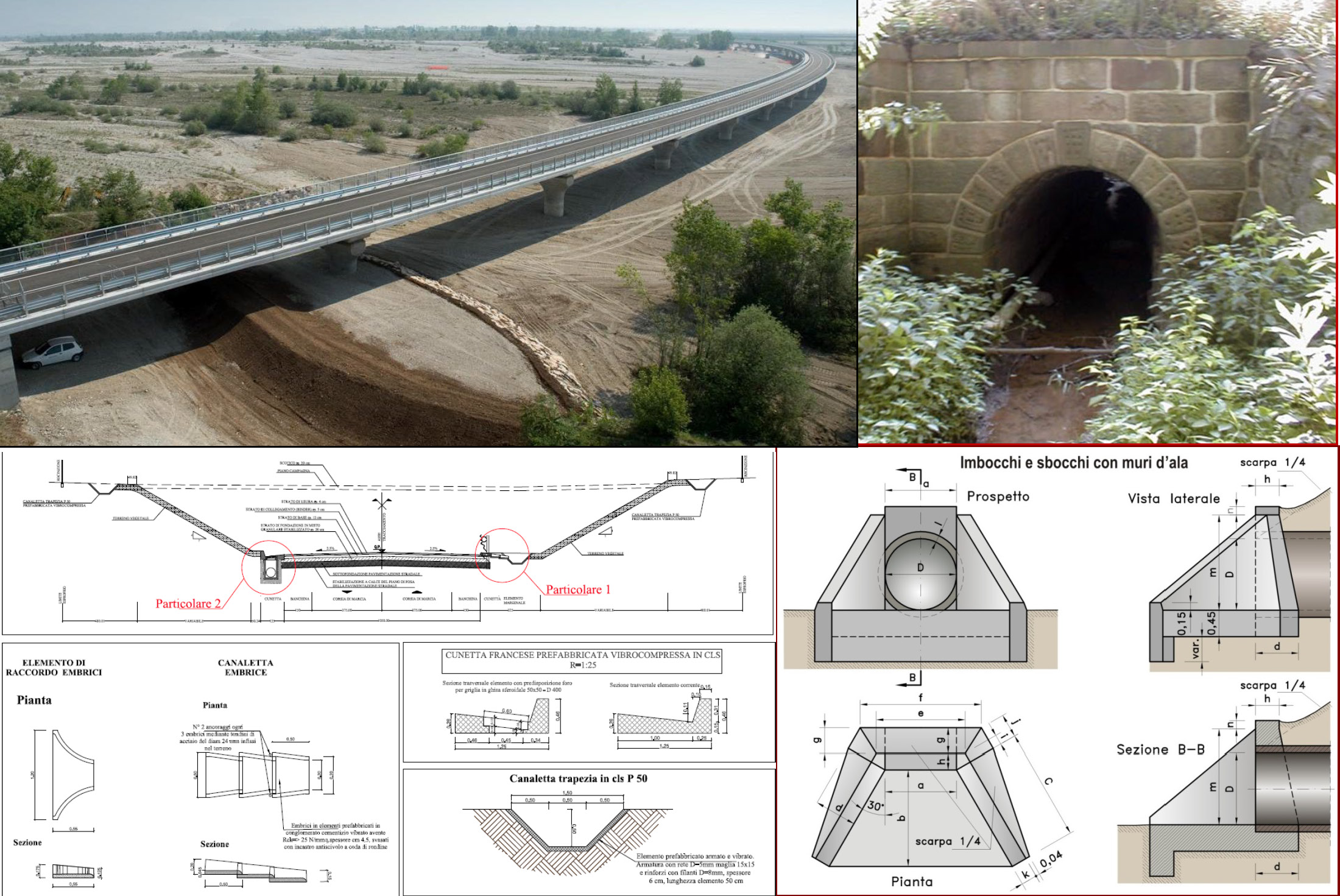
A student who has met the objectives of the course will be able to understand the hydraulic and constructive aspects dealing with the drainage of roads and bridge decks, and the intersections between road and hydrographic network by use of methods, tools and techniques up-to-date. At the end of the course the student will be able to manage the different aspects that concur to the design of that works and to represent the result by use of suitable technical reports and graphical tables.
A student who has met the objectives of the course will be able to understand the hydraulic and constructive aspects dealing with the drainage of roads and bridge decks, and the intersections between road and hydrographic network by use of methods, tools and techniques up-to-date. At the end of the course the student will be able to manage the different aspects that concur to the design of that works and to represent the result by use of suitable technical reports and graphical tables.
- Docente: Paolo Salandin
